Steel pipe coupling is a very short length of tube used in piping or plumbing, it usually refers to the socket weld or a threaded on one or both ends that allows two tubes connected together.

Socket Weld Full Coupling

Threaded Full Coupling
Material Types
Normally there are carbon steel coupling and stainless steel coupling.
Carbon Steel Pipe Coupling
For carbon steel pipe coupling the material standard is ASTM A105, manufacturing standard ASME B16.11.
(There are also casing and tubing coupling material in carbon steel, referred API 5CT J55/K55, N80, P110 etc).
Stainless Steel Pipe Coupling
For stainless steel coupling material standard is ASTM A182, grades in F304/L or 316/L
Application types
As we mentioned above there are:
Socket weld coupling
Threaded coupling
One end in socket weld another end in threaded
And for all of these types for different applications, the are ranges:
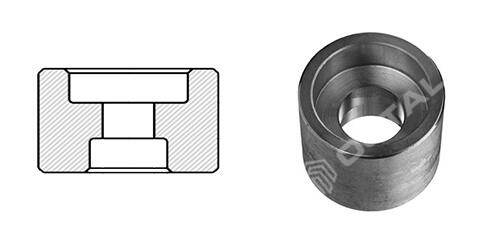
Full Coupling: Joint two pipe or joint pipe to a nipple. (Threaded full coupling is same shape but just ends in threaded)
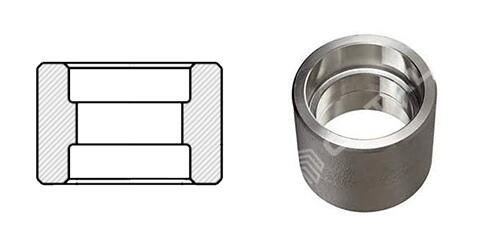
Half Coupling: Joint one end anther end will be welded directly to the run pipe.
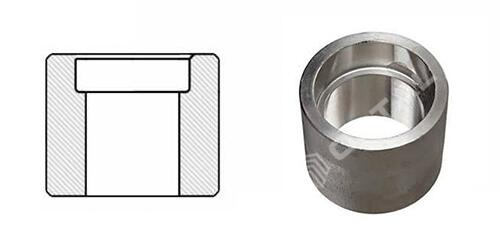
Reducing Coupling:Joint different diameter of pipes.
Differences between Half Coupling vs Full Coupling
Half coupling is only threaded or socket weld at one end, and the other end can be welded directly into the operation of the pipe to form a branch connection. It is a joint that helps to extend or terminate a pipe.
On the other hand, full coupling have both ends of threaded or socket welded.
Threaded Coupling Ends Design (NPT or BSP)
In case of the threaded coupling, the coupling ends normally in female of NPT (National Pipe Threads) or in male and female BSP (British Standard Pipe Threads). Where in North American term, a coupler is a double female while a nipple is double male.
So there are several variation types:
Coupling has one end threads in NPT another end in BSP, then an adapter shall be used during installation.
Coupling has one end in socket weld, another end in threaded socket.
One end in bigger NPT another in smaller dia NPT. (Also called reducing coupling or reducer coupling)
Manufacturing Methods for Coupling and Half Coupling
There are two manufacturing methods: Forging and Casting
Forging process: Raw material as steel ingot or a round bar, heating and forging. After that do threading or not as required. (Applied for carbon, alloy and stainless steel material)
Casing process: Melting the steel ingot and pouring it into a fixed mode and cooling it. (Applied for cast iron material)
Our Supply Ranges:
Material in carbon steel under standard ASTM A105 or Stainless steel ASTM A182 Grade F304/L and F316/L:
Dimensions Range (ASME B16.11): 1/4'', 1/2'', 3/4'', 1'', 1 1/2'', 2'', 3'' and up to 4 inch.
Coupling Types: Full Coupling, Half Coupling
Pressure Ratings: 3000#, 6000#, 9000#
Connection Types: Socket Weld, Threaded Coupling(NPT & BSP)
Material in carbon steel under standard API 5CT Casing and Tubing Coupling:
Sizes: Up to 20 inch.
Connection Threads: BTC, EUE, NUE, Premium





